How Next.ID works
Here, we'll go through the core system design concepts of Next.ID and DIDs.
Avatars in Next.ID
Using the secp256k1 curve with the ECDSA algorithm, avatar key pairs are generated for actions on Next.ID (e.g., signing a follow action) applicable to both on-chain and off-chain activities. Next.ID's relation aggregation can map all these actions:
![]()
ProofService
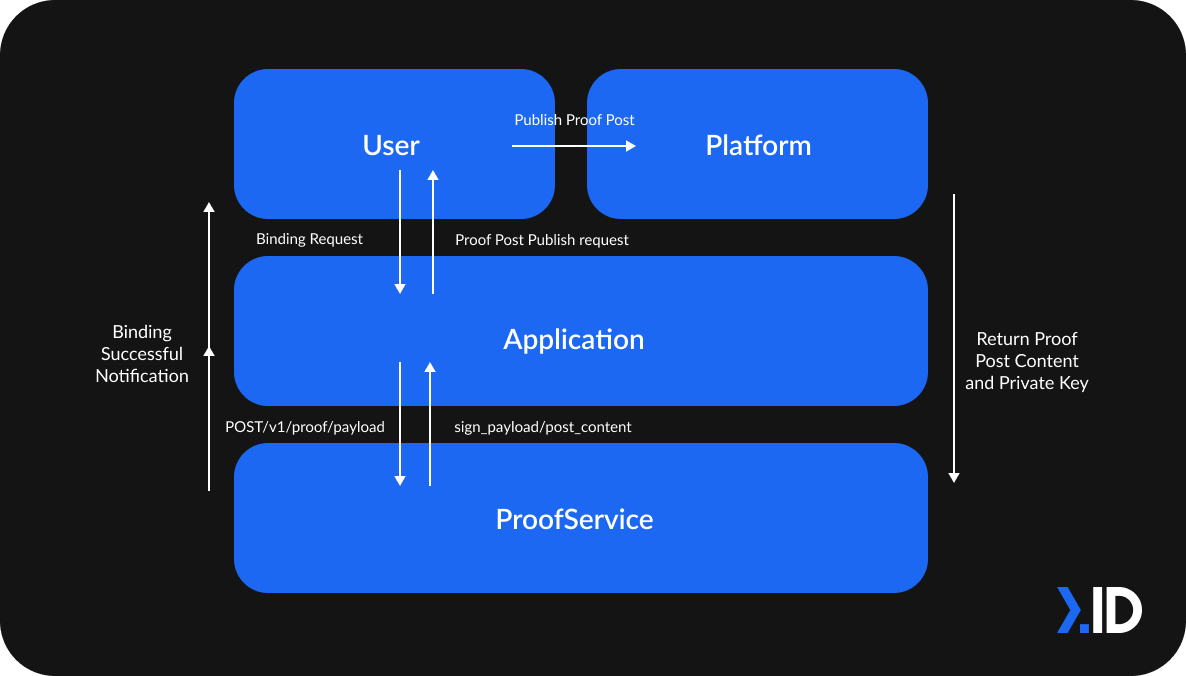
Binding an Avatar to an Application
In this scenario, the user requests an Avatar Binding to an Application, allowing an Avatar to be bound to a user account on the Application. ProofService returns sign_payload and post-content based on the Application’s POST /v1/proof/payload.
Then, the Application requests for the user’s Avatar's Private Key to generate a signature based on sign_payload. Following which, the user publishes the Proof Post on target platforms. The Proof Post link and ID with uuid and created_at will be sent to ProofService per request and be verified from the Application’s post-content.
After ProofService validates the Proof Post's existence and verifies the Private Key, it will relay the successful binding notification back to Application and User.
Example of how it will look like to a user: The user requests for an account (eg: @nextdotid on Twitter) to be bound to their Avatar. The user signs a transaction to authenticate ownership of the account of the Twitter account. Thzte Avatar then generates a public tweet with a signature. When published by the user, this tweet, along with the signature, independently verifies the user's linking of the account to the Avatar.
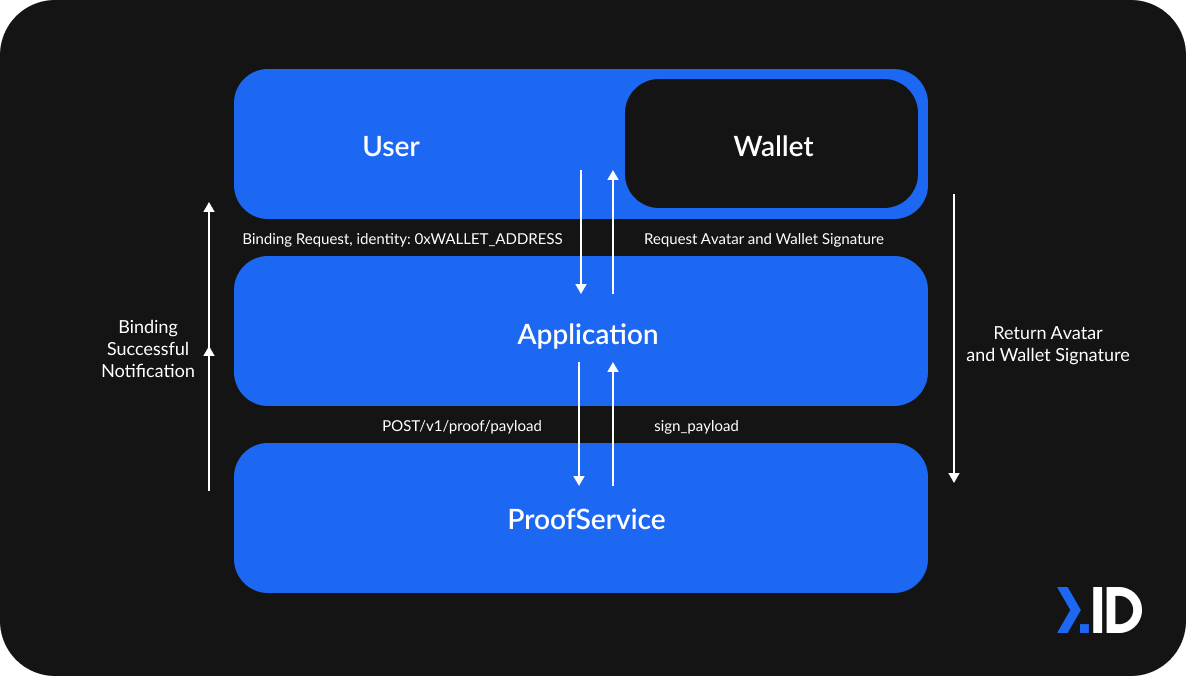
Binding an Avatar to an Application via Ethereum wallet
In this scenario, the user requests an Avatar Binding to an Application with identity 0xWALLET_ADDRESS. ProofService will return the Avatar's sign_payload based on the Application’s POST /v1/proof/payload.
Then, the Application requests the user’s Avatar's Private Key to generate a signature based on Avatarsign_payload. After that, the Application requests user’s Wallet's Private Key to generate a signature based on Walletsign_payload.
ProofServicevalidates the uuid and created_at with sign_payload, then verifies the Avatar's and Wallet's signature. After this, it will relay the successful binding notification back to the Application and User.
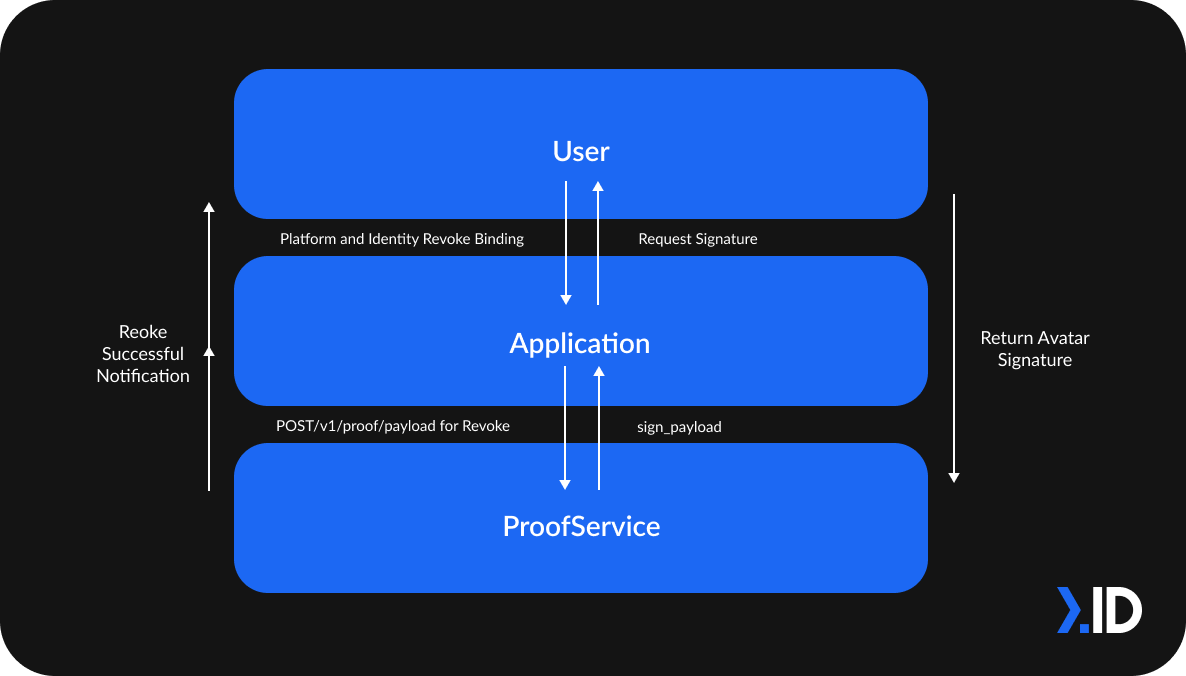
Revoke Binding
In this scenario, User revokes a previously-established Binding made with an Application. ProofService will return the Avatar's sign_payload based on the Application’s POST /v1/proof/payload as a Revoke action.
Then, the Application requests the user’s Avatar Private Key to generate a signature based on sign_payload.
After ProofServicevalidates the signature with uuid and created_at from sign_payload , it verifies the Avatar's and Wallet's signatures for a Revoke action. When this is done, it will relay the successful Revoke notification back to the Application and user.
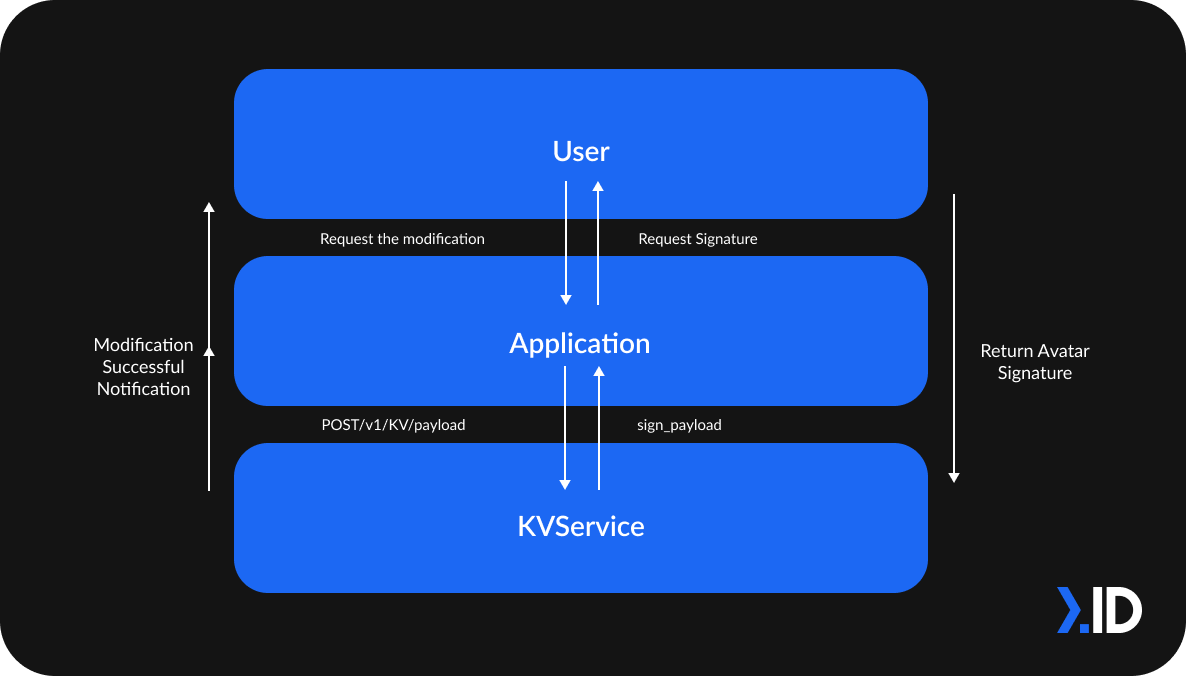
KVService
Write Data
In this scenario, User requests for a modification on an Application. KVService will return the sign_payload based on the Application’s POST /v1/KV/payload.
Then, the application requests the user’s Avatar's Private Key to generate a signature based on sign_payload.
After KVService validates the signature with uuid and created_at from sign_payload , it will then verify the Avatar Signature for the Write Data action. After that, it will relay the successful notification back to Application and User.